Personality Disorder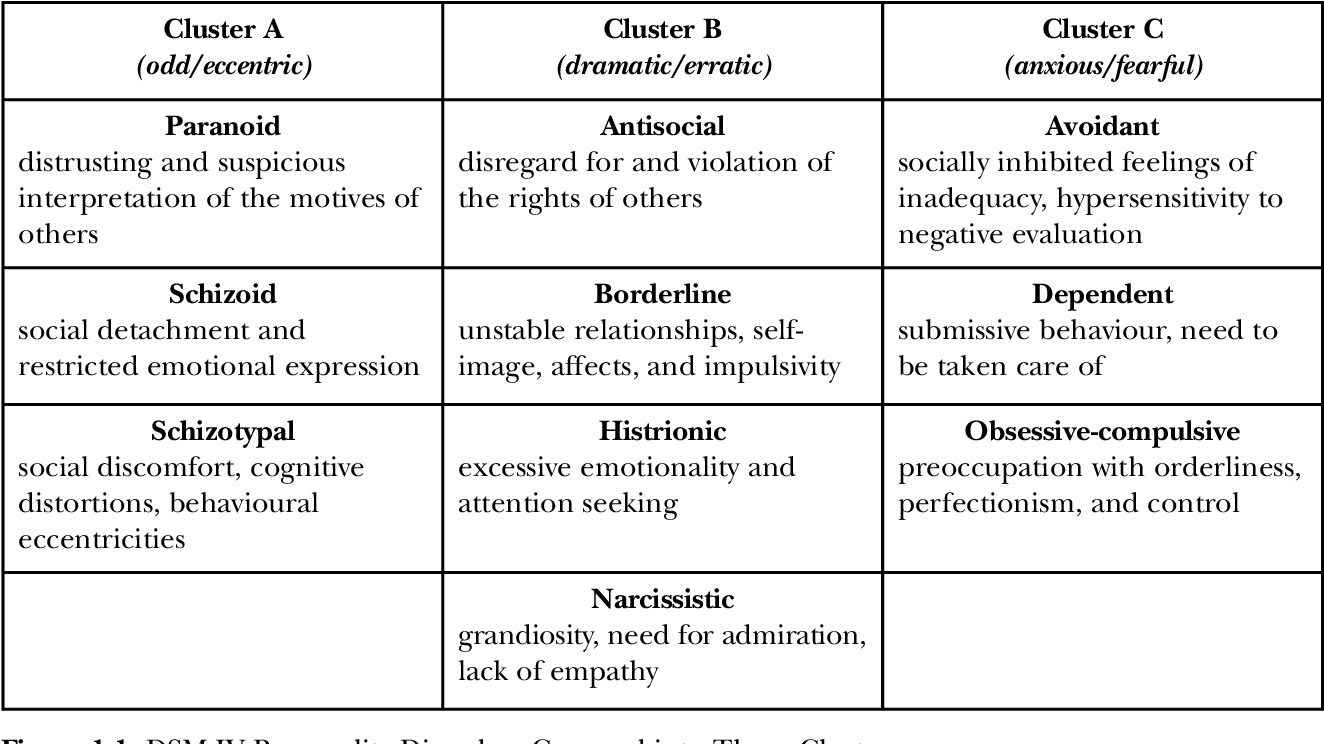
A personality disorder is a type of mental disorder in which you have a rigid and unhealthy pattern of thinking, functioning and behaving. A person with a personality disorder has trouble perceiving and relating to situations and people. This causes significant problems and limitations in relationships, social activities, work and school. In some cases, you may not realize that you have a personality disorder because your way of thinking and behaving seems natural to you. And you may blame others for the challenges you face. Personality disorders usually begin in the teenage years or early adulthood. There are many types of personality disorders. Some types may become less obvious throughout middle age. Some examples of Personality disorders are:
- Cluster A personality disorders involve unusual and eccentric thinking or behaviors. These include:
- Paranoid personality disorder: The main feature of this condition is paranoia, which is a relentless mistrust and suspicion of others without adequate reason for suspicion. People with paranoid personality disorder often believe others are trying to demean, harm or threaten them.
- Schizoid personality disorder: This condition is marked by a consistent pattern of detachment from and general disinterest in interpersonal relationships. People with schizoid personality disorder have a limited range of emotions when interacting with others.
- Schizotypal personality disorder: People with this condition display a consistent pattern of intense discomfort with and limited need for close relationships. Relationships may be hindered by their distorted views of reality, superstitions and unusual behaviors.
- Cluster B personality disorders Cluster B personality disorders involve dramatic and erratic behaviors. People with these types of conditions display intense, unstable emotions and impulsive behaviors. Cluster B personality disorders include:
- Antisocial personality disorder (ASPD): People with ASPD show a lack of respect toward others and don’t follow socially accepted norms or rules. People with ASPD may break the law or cause physical or emotional harm to others around them. They may refuse to take responsibility for their behaviors and/or display disregard for the negative consequences of their actions.
- Borderline personality disorder (BPD): This condition is marked by difficulty with emotional regulation, resulting in low self-esteem, mood swings, impulsive behaviors and subsequent relationship difficulties.
- Histrionic personality disorder: This condition is marked by intense, unstable emotions and a distorted self-image. For people with histrionic personality disorder, their self-esteem depends on the approval of others and doesn’t come from a true feeling of self-worth. They have an overwhelming desire to be noticed by others, and may display dramatic and/or inappropriate behaviors to get attention.
- Narcissistic personality disorder: This condition involves a consistent pattern of perceived superiority and grandiosity, an excessive need for praise and admiration and a lack of empathy for others. These thoughts and behaviors often stem from low self-esteem and a lack of self-confidence.
- Cluster C personality disorders Cluster C personality disorders involve severe anxiety and fear. They include:
- Avoidant personality disorder: People with this condition have chronic feelings of inadequacy and are highly sensitive to being negatively judged by others. Though they would like to interact with others, they tend to avoid social interaction due to the intense fear of being rejected.
- Dependent personality disorder: This condition is marked by a constant and excessive need to be cared for by someone else. It also involves submissiveness, a need for constant reassurance and the inability to make decisions. People with dependent personality disorder often become very close to another person and spend great effort trying to please that person. They tend to display passive and clinging behavior and have a fear of separation.
- Obsessive-compulsive personality disorder (OCPD): This condition is marked by a consistent and extreme need for orderliness, perfectionism and control (with no room for flexibility) that ultimately slows or interferes with completing a task. It can also interfere with relationships. This is a separate condition from obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), which is classified as an anxiety disorder. While people with OCD usually are aware that OCD is causing their behavior and accept they need to change, people with OCPD usually have little, if any, self-awareness of their behaviors.
Get started with therapy at People to People today.
